Company & User Information
ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS
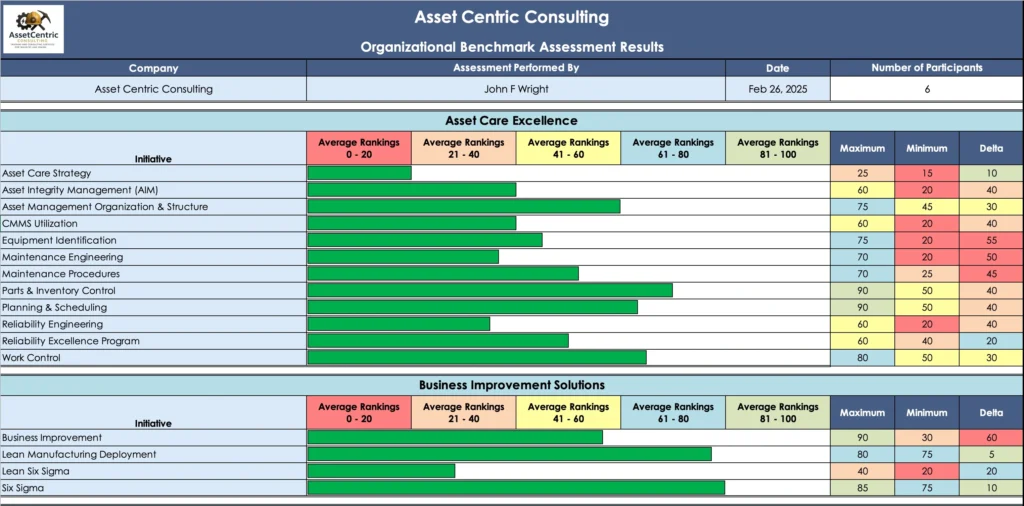
Asset Care Strategy
Asset Integrity Management
Asset Management Organization & Structure
CMMS Utilization
Equipment Identification
Maintenance Engineering
Parts & Inventory Control
Planning & Scheduling
Reliability Engineering
Reliability Excellence Program
Work Control
Business Improvement
Lean Manufacturing
Lean Six Sigma
Six Sigma
Contractor Control
Employee Skills & Training
Health, Safety, the Environment & Community (HSEC) Stewardship
Human Resources (HR) Development
Roles & Responsibilities
Cultural Change Management
Leadership Development
Management Commitment
MSHA & OSHA Certified Training
Business Resilience & Continuity Plan
Capital Budget & Control
Continuous Improvement
Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG)
Financial Analysis & Planning
Management of Change (MOC)
Operating Budget & Control
Operating Procedures
Overall Equipment Effectiveness
Performance Metrics
Procurement
Production Planning
Technical Services
Threats, Risk & Opportunity Analysis Management
Visual Management
Warehouse
Operational Readiness (OR) Deployment
Design for Reliability, Operability, & Maintainability (DROM)
132. Project & Management Deployment
Project Portfolio Management